Bubble Sort Algorithm in DSA
Last modified - 30-05-2025
Author - Krishna Shinde
When you start your journey as a beginner in Data Structures and Algorithms, You will encounter various sorting algorithms one of which is the Bubble Sort Algorithm. In this tutorial, we will deep dive into the Bubble Sort concept in data structures and provide codes of the Bubble Sort algorithm in C++ and C to help you understand it better.
Bubble Sort Explained
Bubble Sort is a simple comparison-based sorting algorithm. It repeatedly iterates the array, compares an element with its next element, and swaps them if the first element is greater than the next element. This process is repeated until the array becomes sorted. The largest element “bubbles up” to its correct position with each pass, which is where the name comes from.
How Does Bubble Sort Work
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of the Bubble Sort algorithm:
- Start with the first element.
- Compare the current element with the next element.
- If the current element is greater than the next, swap them.
- Move to the next pair and repeat steps 2-3 for the rest of the array.
- After each complete pass, the largest unsorted element moves to its correct position at the end.
- Continue the passes until no swaps are needed, indicating the array is sorted.
Bubble Sort C++ Program
Here is a clean and optimized Bubble Sort algorithm in C++:#include <iostream> using namespace std; void bubbleSort(int arr[], int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) { bool swapped = false; for (int j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++) { if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]) { swap(arr[j], arr[j+1]); swapped = true; } } if (!swapped) break; // Stop if array is already sorted } } void printArray(int arr[], int size) { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) cout << arr[i] << " "; cout << endl; } int main() { int arr[] = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90}; int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]); bubbleSort(arr, n); cout << "Sorted array: "; printArray(arr, n); return 0; }
Bubble Sort C Program
Here’s a simple C program of Bubble Sort Algorithm:
#include <stdio.h> void bubbleSort(int arr[], int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) { int swapped = 0; for (int j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++) { if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]) { int temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j+1]; arr[j+1] = temp; swapped = 1; } } if (swapped == 0) break; } } void printArray(int arr[], int size) { for (int i=0; i < size; i++) printf("%d ", arr[i]); printf(" "); } int main() { int arr[] = {5, 1, 4, 2, 8}; int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]); bubbleSort(arr, n); printf("Sorted array: "); printArray(arr, n); return 0; }
Time Complexity of Bubble Sort
| Case | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best Case | O(n) | O(1) | Stable |
| Average Case | O(n²) | O(1) | Stable |
| Worst Case | O(n²) | O(1) | Stable |
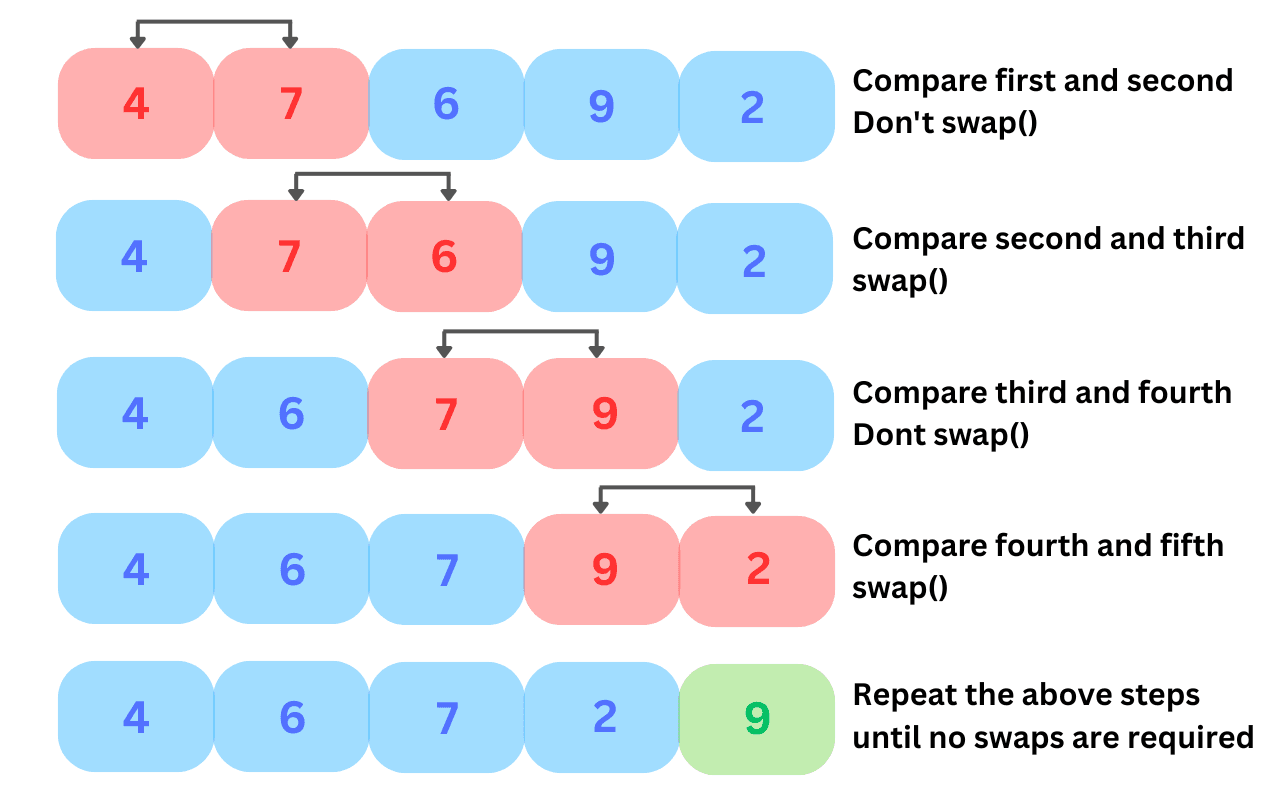
Bubble Sort Example Step by Step
Let's do a manual run through of the Bubble Sort technique with the array: [5, 1, 4, 2, 8].
First pass:
- Compare 5 and 1 → Swap → [1, 5, 4, 2, 8]
- Compare 5 and 4 → Swap → [1, 4, 5, 2, 8]
- Compare 5 and 2 → Swap → [1, 4, 2, 5, 8]
- Compare 5 and 8 → No swap
Second pass:
- Compare 1 and 4 → No swap
- Compare 4 and 2 → Swap → [1, 2, 4, 5, 8]
- Compare 4 and 5 → No swap
Third pass:
- Compare 1 and 2 → No swap
- Compare 2 and 4 → No swap
No swaps in the third pass, the array is now sorted.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bubble Sort
Advantages:
- Simple and easy to implement.
- Best-case performance is relatively good for nearly sorted arrays.
- Requires no extra space other than the temporary variables.
Disadvantages:
- Not good for large datasets.
- Poor time complexity compared to advanced algorithms like Quick Sort or Merge Sort.
When to Use Bubble Sort?
Bubble sort is not efficient for large datasets, but can be used in scenarios like:
- Teaching and learning basic DSA concepts.
- Sorting very small or nearly sorted datasets.
- Situations where code simplicity matters more than performance.
- In professional coding interviews, understanding the workings of Bubble Sort and being able to optimize it shows strong foundational knowledge.
Conclusion
Bubble Sort is a simple, easy-to-understand sorting algorithm that cannot be used for large datasets, but knowing how to optimize and implement bubble sort can increase your fundamental knowledge. We have already written an article on selection sort, and explore our DSA tutorial blogs. Follow Algoflame for more programming content.