Structure of C++ Program
Last modified - 09-12-2025
Author - Krishna Shinde
A C++ program follows a defined structure, that is later compiled into binary by the compiler, This is how the structure of the C++ program is followed:
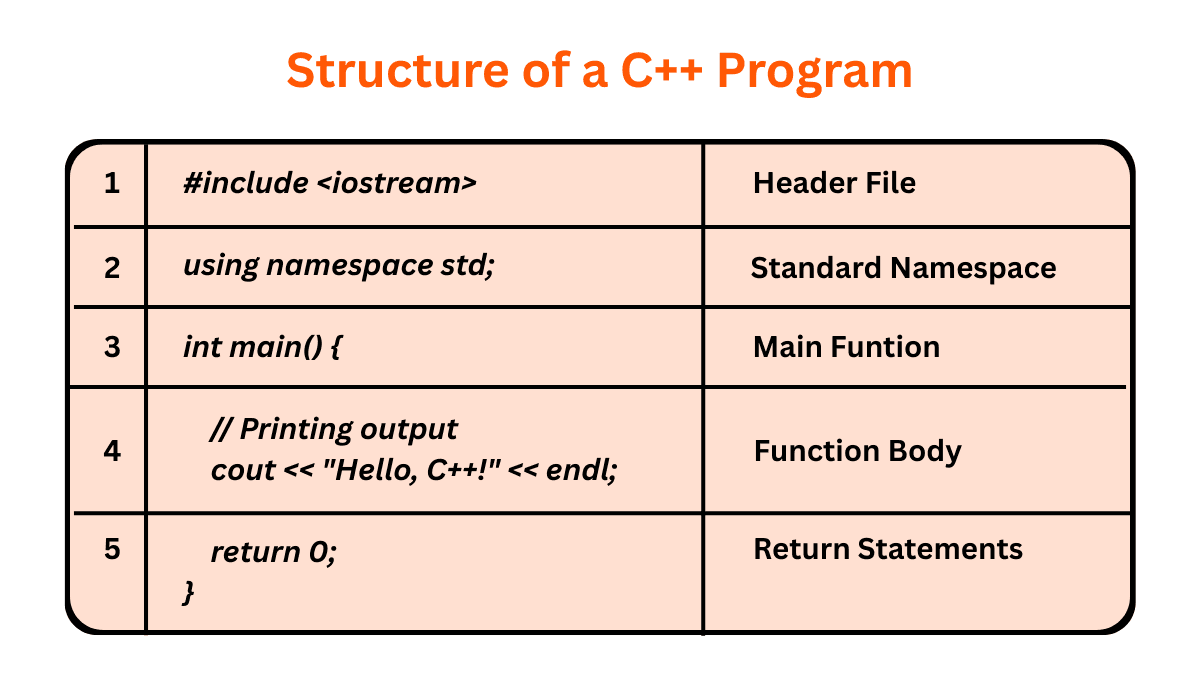
Header File
#include <iostream>
The header files provide predefined functions that can be reused in our program, iostream is a standard input - output library in C++ that allows us to print the output using cout and take input from the user using cin.
If iostream is not included the compiler will not understand the cout and cin command.
Namespace Declaration
using namespace std;
Std is a keyword which stands for standard namespace. C++ stores its standard library functions like cout, cin, string in std namespace.
If the standard namespace is not declared we need to write std everytime before using standard library functions.
Before declaring namespace std
std::cout << "Hello, Algoflame!";
After declaring namespace std
cout << "Hello, Algoflame!";
Using namespace makes the code shorter and readable.
Main Function
int main(){}
The execution of the program starts from the main function. Every C++ program must have the main function.
The int before the main indicates that the function on execution returns an integer value to the operating system, thus the return type of main in int.
The empty parentheses () after main indicate that the function does not take any arguments.
Body of main function
The body consists of all executable statements - variable declaration, logic, and output.
Why braces are used in programming
The curly braces define the block of the code; they tell the compiler where a function, a loop, or a conditional block begins and ends.
int main() { // Block begins // body of main function } // Block ends
Comments in C++
// Single line comment /* Multi line comment */
Comments are the statements ignored by the compilers on execution of the code. They are used to explain the code, document the code and improve readability, especially in large programs.
There are two types of comments in C++, single line comment and multi line comment.
Statements in C++
cout << "Hello, Algoflame!";
Statements are the instructions that are executed by the compilers. A statement ends with a semicolon. Statements in programming are used for variable declaration, assigning values, calling function, taking input, printing output, etc.
Return Statement
return 0;
The return statement ends the main function and returns the value to the operating system. When a return statement is encountered the function is terminated.
Conclusion
A C++ program always follows this order:
- Header files inclusion
- Namespace declaration
- Main function
- Body of main function
- Return statement